1.引言
征程6 工具链目前已经提供了比较丰富的集成化工具和接口来支持模型的移植和量化部署,本帖将整理常用的工具/接口以及使用示例来供大家参考,相信这篇文章会提升大家对 征程6 工具链的使用理解以及效率。
干货满满,欢迎访问
2.hb_config_generator
hb_config_generator 是用于获取模型编译最简 yaml 配置文件、包含全部参数默认值的 yaml 配置文件的工具。使用示例:
hb_config_generator --full-yaml --model model.onnx --march nash-e
3.hb_compile
hb_compile是 PTQ 中集模型验证、模型修改和编译工具。使用前确保您的环境中已经安装了 horizon_tc_ui,horizon_nn(后面将更新为 hmct)和 hbdk4-compiler。相关使用示例如下:
3.1 模型验证
#单输入
hb_compile --march ${march} \
--proto ${caffe_proto} \
--model ${caffe_model/onnx_model} \
--input-shape ${input_node_name} ${input_shape}
#多输入
hb_compile --march ${march} \
--proto ${caffe_proto} \
--model ${caffe_model/onnx_model} \
--input-shape input.0 1x1x224x224
--input-shape input.1 1x1x224x224
--input-shape input.2 1x1x224x224
3.2 模型修改
出于某些极大尺寸输入场景下的极致性能需求,部分输入/输出端的量化和转置操作可以融合在数据前处理中一并完成。 此时可以选择在 yaml 中配置 remove_node_type 参数,然后使用 hb_compile 工具移除这些节点,同时 hb_compile 工具还支持对 HBIR 模型的编译。
hb_compile --config ${config_file} \
--model ${model.bc}
3.3 模型量化编译
使用 hb_compile 工具对模型进行量化编译时,提供两种模式,快速性能评测模式(开启 fast-perf)和传统模型转换编译模式(不开启 fast-perf)。
fast-perf
快速性能评测模式开启后,会在转换过程中生成可以在板端运行最高性能的 hbm 模型:
hb_compile --fast-perf --model ${caffe_model/onnx_model} \
--proto ${caffe_proto} \
--march ${march} \
--input-shape ${input_node_name} ${input_shape}
传统方式
hb_compile --config ${config_file}4.hb_verifier
hb_verifier 是一致性验证工具,支持进行 onnx 模型之间、onnx 模型与 hbir 模型、hbir 模型与 hbir 模型之间的余弦相似度对比, bc 与 Hbm 模型之间的输出一致性对比。
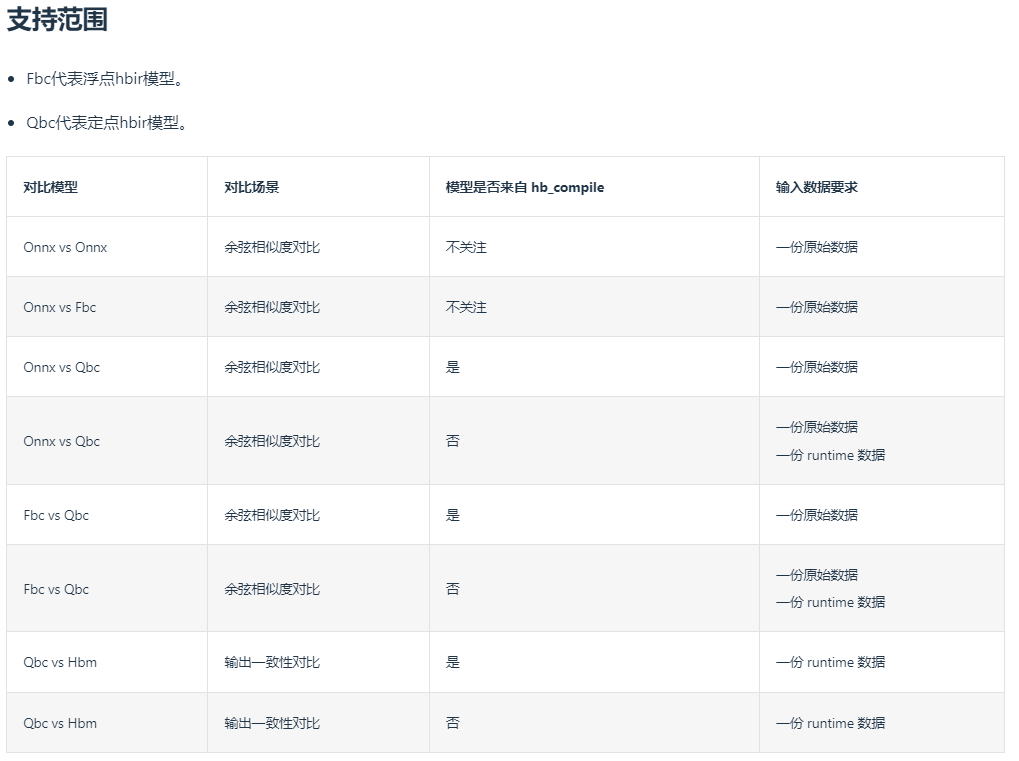
使用示例如下:
ONNX 模型与 ONNX 模型之间进行余弦相似度对比。
以模型优化阶段模型 optimized_float_model.onnx 与模型校准阶段模型 calibrated_model.onnx 为例:
hb_verifier -m googlenet_optimized_float_model.onnx,googlenet_calibrated_model.onnx -i input.npy
2.ONNX 模型与 HBIR 模型之间进行余弦相似度对比。
以模型优化阶段模型 optimized_float_model.onnx 与模型量化阶段定点模型 quantized_model.bc 为例:
hb_verifier -m googlenet_optimized_float_model.onnx,googlenet_quantized_model.bc -i input.npy
3.HBIR 模型与 HBM 模型之间进行输出一致性对比。
以模型量化阶段定点模型 quantized_model.bc 与模型编译阶段模型 googlenet.hbm为例:
hb_verifier -m googlenet_quantized_model.bc,googlenet.hbm -i runtime_input.npy
5.hb_model_info
hb_model_info 是用于解析。hbm 和。bc 编译时的依赖及参数信息、。onnx 模型基本信息,同时支持对。bc 可删除节点进行查询的工具。使用示例如下:
#输出bc模型/hbm的输入输出信息
hb_model_info model.bc/model.hbm
#输出bc模型/hbm的输入输出信息并在隐藏文件夹生成onnx/prototxt
hb_model_info model.bc/model.hbm -v
6.伪量化 bc 导出
6.1ONNX export
编译器的onnx.export接口提供了可以将 onnx 模型转为 bc 模型的功能,使用示例如下:
import onnx
from hbdk4.compiler.onnx import export
from hbdk4.compiler import convert,save
#加载onnx模型
ptq_onnx = onnx.load("xx_ptq_model.onnx")
#export为bc模型
bc_model = export(ptq_onnx)
#保存bc模型
save(bc_model,"model.bc")
6.2Torch export
编译器的torch.export接口提供了可以将 torch 模型转为 bc 模型的功能,使用示例如下:
import torch
import torchvision
from hbdk4.compiler.torch import statistics as torch_statistics
from hbdk4.compiler.torch import export
from hbdk4.compiler import save
# 载入浮点resnet
module = torchvision.models.resnet18(pretrained=True)
example_input = torch.rand(1, 3, 224, 224)
module = torch.jit.trace(module, example_input)
torch_statistics(module, example_input) # 打印torch op列表和数量
# 将torchscript导出为bc
exported_module = export(module, example_input, name="TorchModel", input_names=["image"], output_names=["pred"])
save(exported_modul,"model.bc")
或者使用地平线 QAT 封装的编译器 export 接口(horizon_plugin_pytorch.quantization.hbdk4.export)来导出伪量化 bc,接口介绍如下:
horizon_plugin_pytorch.quantization.hbdk4.export(model: Module, example_inputs: Any, *, name: str = 'forward', input_names: Any | None = None, output_names: Any | None = None, input_descs: Any | None = None, output_descs: Any | None = None)
Export nn.Module to hbir model.
Parameters:
--model – Input model.#输入的伪量化模型,需要是eval()后的
--example_inputs – Example input for tracing.#给定的作为trace的输入
--name – The name of func in exported module. Users can get the func by getattr(hbir_module, name).#导出的bc的名称
--input_names – Set hbir inputs with given names, should have the same structure with example_inputs.#导出的bc的输入名称
--output_names – Set hbir outputs with given names, should have the same structure with model output.#导出的bc的输出名称
--input_descs – Set hbir inputs with given descriptions, should have the same structure with example_inputs.#导出的bc的输入描述信息,用户可自定义,板端部署时使用
--output_descs – Set hbir outputs with given descriptions, should have the same structure with model output.##导出的bc的输出描述信息,用户可自定义,板端部署时使用,例如anchor的score信息等
Returns: Hbir model wrapped with Module.
7.bc 模型加载、修改、定点化、编译、perf
编译器提供了 bc 模型加载、定点化、编译的相关接口。

下面将以一个完整的示例来讲述以上接口的使用:
from hbdk4.compiler.torch import export
from hbdk4.compiler import statistics, save, load,visualize,compile
from hbdk4.compiler.march import March
from hbdk4.compiler import convert,hbm_perf
#使用load加载伪量化bc
model=load("qat.bc")
#使用visualize生成onnx可视化bc
visualize(model, "qat_ori.onnx")
func = model.functions[0]
#batch拆分,此过程为batch nv12输入的必须操作
batch_input = ["_input_0"]
for input in func.inputs[::-1]:
for name in batch_input[::-1]:
if name in input.name:
input.insert_split(dim=0)
#可视化已做完batch拆分的bc
visualize(model, "qat_split_batch.onnx")
#插入预处理节点
func = model.functions[0]
#pyramid_input为模型中NV12输入的name,可以通过可视化qat_split_batch.onnx获取
#ddr_input为模型中ddr输入的name,可以通过可视化qat_split_batch.onnx获取
pyramid_input = ['_input_0_0','_input_0_1','_input_0_2','_input_0_3','_input_0_4','_input_0_5'] # 部署时数据来源于pyramid的输入节点名称列表
ddr_input = "_input_1" # 部署时数据来源于ddr的输入节点名称列表
#插入nv12节点
for input in func.inputs[::-1]:
print(input.name)
if input.name in pyramid_input:
#pyramid&resizer 只支持 NHWC 的 input layout
input.insert_transpose(permutes=[0, 3, 1, 2])
# 插入前处理节点,这里模型训练是YUV444图像,所以mode配置为None
input.insert_image_preprocess(mode=None, divisor=1, mean=[128, 128, 128], std=[128, 128, 128])
input.insert_image_convert("nv12")
print("-----insert nv12 success-----")
#插入resizer节点
#for input in func.inputs[::-1]:
#if input.name in resizer_input:
# pyramid&resizer 只支持 NHWC 的 input layout
#node = input.insert_transpose(permutes=[0, 3, 1, 2])
# 插入前处理节点,具体可参考下一节的说明
#node = input.insert_image_preprocess(mode=None, divisor=1, mean=[128, 128, 128], std=[128, 128, 128])
#node.insert_roi_resize("nv12")
#插入transpose节点
for input in func.inputs[::1]:
if input.name == ddr_input:
#layerout变换:NCHW->NHWC
input.insert_transpose(permutes=[0, 2, 3, 1])
#可视化插入预处理节点后的模型
visualize(model, "qat_preprocess.onnx")
#将插入预处理节点后hbir保存为bc
save(model,"qat_preprocess.bc")
#将伪量化bc convert为定点bc
#配置advice参数显示算子相关信息
quantized_model=convert(model,'nash-e',advice=True,advice_path='./')
#可视化定点bc
visualize(quantized_model, "quantized_ori.onnx")
#删除量化/反量化节点
# convert后的bc的首尾部默认包含量化反量化节点,可以进行手工删除
node_type_mapping = {
"qnt.quantize": "Quantize",
"qnt.dequantize": "Dequantize",
"hbir.transpose": "Transpose",
"hbtl.call::quant::qcast": "Quantize",
"hbtl.call::quant::dcast": "Dequantize",
"hbtl.call::native::Transpose": "Transpose",
"hbir.cast_type": "Cast",
"hbir.reshape": "Reshape",
"hbtl.call::native::Cast": "Cast",
"hbtl.call::native::Reshape": "Reshape",
}
def get_type_for_hbtl_call(attached_op):
schema = attached_op.schema
node_type = attached_op.type + "::" + \
schema.namespace + "::" + schema.signature
return node_type
def remove_op(func, op_type=None, op_name=None):
for loc in func.inputs + func.outputs:
if not loc.is_removable[0]:
continue
attached_op = loc.get_attached_op[0]
removed = None
# 目前hbir模型中的op name格式还未完全确定,暂建议使用op type来删除节点
attached_op_name = attached_op.name
if op_name and attached_op.name in op_name:
removed, diagnostic = loc.remove_attached_op()
elif op_type and attached_op.type in node_type_mapping.keys() \
and node_type_mapping[attached_op.type] in op_type:
removed, diagnostic = loc.remove_attached_op()
elif attached_op.type == "hbtl.call":
# 由于同一type的op在后端可能对应多种实现,因此采用“签名”的方式确认具体类型
node_type = get_type_for_hbtl_call(attached_op)
if op_type and node_type in node_type_mapping.keys() \
and node_type_mapping[node_type] in op_type:
removed, diagnostic = loc.remove_attached_op()
if removed is True:
print(f'Remove node', op_type, "successfully")
if removed is False:
raise ValueError(f'Remove node type', op_type,
f"Failed when deleting {attached_op.name} operator,"
f"error: {diagnostic}")
func = quantized_model[0]
# 删除reshape节点
#remove_op(func, op_type="Reshape")
#remove_op(func, op_type="Cast")
# 删除量化反量化节点
remove_op(func, op_type="Dequantize")
remove_op(func, op_type="Quantize")
# 删除max后的reshape节点
#remove_op(func, op_type="Reshape")
# 删除Transpose节点
#remove_op(func, op_type="Transpose")
print("-----remove_quant_dequant OK-----")
save(quantized_model,"quantized_modified.bc")
visualize(quantized_model, "quantized_remove_dequa.onnx")
#使用compile编译定点bc为hbm
print("-----start to compile model-----")
#
params = {'jobs': 48, 'balance': 100, 'progress_bar': True,
'opt': 2,'debug':True}
compile(
quantized_bc,
march="nash-e",
path="model.hbm",
**params
)
print("-----end to compile model-----")
#模型性能预估
print("-----start to perf model-----")
save_path="./perf"
hbm_perf('model.hbm',save_path)
这样,我们就完成了伪量化 bc 的加载、修改、量化编译和性能预估的过程。
*博客内容为网友个人发布,仅代表博主个人观点,如有侵权请联系工作人员删除。